What is Melanoma?
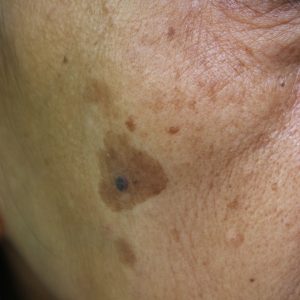
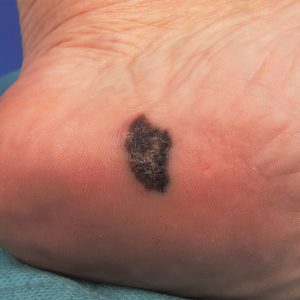
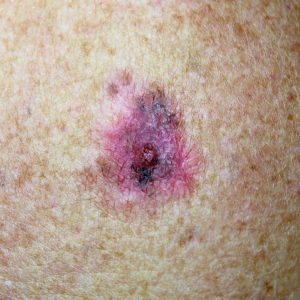
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in skin cells called melanocytes – the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. These cells are located in the upper layer of the skin and can mutate into cancer cells when damaged by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Damage tends to occur on body parts that are exposed to excessive sunlight, but melanoma can also develop in areas not regularly exposed. It’s commonly thought that melanoma only affects moles on the skin. However, melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin – even in areas not easily visible.
At Montserrat Medical Services, we deliver advanced, patient-focused care for early melanoma diagnosis and surgical treatments. Our expert team of surgeons and state-of-the-art facilities mean you will always get a safe and comfortable experience, so you can expect peace of mind throughout – from diagnosis through to recovery.